Exploring the Advanced Features of Modern Galvanometer Scanners in Research Study
Exploring the Advanced Features of Modern Galvanometer Scanners in Research Study
Blog Article
Trick Applications of a Galvanometer Scanner in Numerous Scientific Research Area
Galvanometer scanners have become indispensable to various scientific study fields, providing improved precision in applications varying from biomedical imaging to ecological monitoring. Their ability to assist in high-resolution imaging methods, such as confocal microscopy, plays a crucial duty beforehand our understanding of mobile structures. In product handling, these tools improve the accuracy of laser cutting and welding. As we discover the diverse applications of galvanometer scanners, it comes to be apparent that their impact prolongs far past simple technical abilities, questioning about their future possibility in arising research areas.
Biomedical Imaging

In confocal microscopy, galvanometer scanners help with the procurement of pictures with enhanced resolution and comparison, allowing researchers to picture mobile components in vivo. The capacity to swiftly record numerous focal airplanes enhances the three-dimensional repair of tissues, providing crucial understandings right into their style and function.

Moreover, the quick scanning capacities of galvanometer systems contribute to developments in dynamic imaging applications, such as keeping track of cellular actions to stimuli. Hence, galvanometer scanners are important tools in the field of biomedical imaging, advancing study and professional diagnostics with their precision and effectiveness.
Material Handling
Precision in material handling is critical for achieving top quality results in various commercial applications (galvanometer scanner). Galvanometer scanners play a vital role in improving this precision by making it possible for precise and quick movement control throughout the processing of materials such as polymers, ceramics, and steels. These devices assist in methods like laser welding, inscription, and cutting, which call for finely-tuned changes to make sure optimal end results
In laser cutting, for circumstances, galvanometer scanners permit complex designs to be performed with high integrity, decreasing waste and enhancing production effectiveness. The rapid activity capacities make it possible for quick changes in the laser light beam course, which is essential for keeping constant reducing quality throughout varying material densities. In laser welding applications, the precision used by galvanometer scanners makes certain solid joints with marginal thermal distortion, thereby improving architectural honesty.
In addition, the adaptability of galvanometer scanners to various laser kinds and wavelengths better widens their utility in product handling. Their capacity to operate in tandem with advanced software program for real-time monitoring and control adds an extra layer of refinement, allowing makers to achieve precise specifications tailored to specific applications. Therefore, galvanometer scanners are vital in advancing the abilities of material handling innovations.
Optical Characterization
In the world of optical characterization, the duty of galvanometer scanners comes to be significantly significant as they assist in the evaluation of various optical residential properties with high accuracy. These tools enable specific control of laser beam of lights, allowing scientists to systematically penetrate products at numerous angles and regularities. This capability is crucial for identifying the refractive index, absorption coefficient, and spreading residential or commercial properties of varied materials.
Galvanometer scanners are particularly reliable in strategies such as optical comprehensibility tomography (OCT) and laser-induced fluorescence (LIF), where rapid scanning is important. By achieving high-speed modulation of the laser placement, galvanometer scanners enhance the temporal resolution of these techniques, bring about enhanced imaging and evaluation. Furthermore, they allow the exploration of intricate communications between light and issue, which is essential for understanding product actions under different problems.
In addition, the integration of galvanometer scanners with spectroscopic techniques expands their utility, allowing for extensive spectral analysis across a vast blog array of wavelengths. This convenience makes them important tools in fields such as materials scientific research, biomedical research, and nanotechnology, where thorough optical characterization is paramount for progressing understanding and technology.
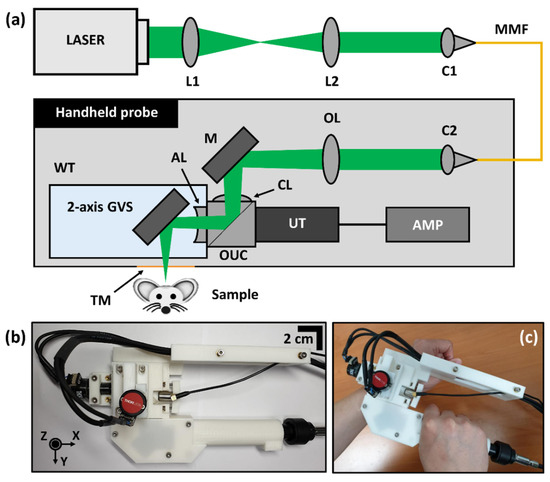
Laser Micromachining
The advent of laser micromachining has changed producing procedures, making it possible for the development of detailed structures with unparalleled accuracy. This strategy makes use of high-intensity laser light beams to precisely eliminate material from a substrate, making it possible to fabricate micro-scale navigate to this website elements that are crucial in various markets. The application of galvanometer scanners in laser micromachining enhances the efficiency and precision of this procedure by allowing quick and precise beam positioning.
Galvanometer scanners help with the vibrant control of laser beam of lights, making it possible for complicated patterns to be engraved or cut with high integrity. Their quick feedback times and high-resolution capabilities enable the adjustment of laser pulses, which is necessary for achieving the desired product properties and surface coatings. This innovation is specifically useful in sectors such as electronics, where the miniaturization of elements is crucial for performance improvement.
Additionally, laser micromachining is significantly being utilized in the medical field for making accuracy instruments and implants. The mix of laser modern technology and galvanometer scanning not only simplifies manufacturing workflows but additionally reduces waste and improves overall material utilization, making it a sustainable choice for modern manufacturing obstacles.
Ecological Surveillance
Environmental monitoring has ended up being increasingly important in analyzing and handling the health and wellness of communities and urban settings. The combination of galvanometer scanners in this area makes it possible for accurate, fast, and effective information collection, facilitating better decision-making processes. These scanners are experienced at guiding laser beam of lights or sensors throughout numerous terrains, enabling high-resolution mapping of ecological criteria such as air high quality, dirt composition, and water contamination.
In air high quality surveillance, galvanometer scanners can be employed to analyze particle matter and gaseous toxins, offering real-time data that educates public health and wellness initiatives. For water quality analyses, these scanners can assist in identifying contaminants and gauging physical specifications, therefore guaranteeing conformity with environmental policies. Furthermore, in remote noticing applications, galvanometer scanners enhance the capability of satellite and Recommended Reading drone systems to record in-depth photos and data of substantial areas, determining environmental adjustments and anthropogenic impacts.
The flexibility and accuracy of galvanometer scanners make them essential devices in ecological monitoring, contributing substantially to sustainable advancement initiatives and the security of natural deposits. As the requirement for reliable ecological management grows, the role of these advanced gadgets will most certainly expand additionally.
Conclusion
In recap, galvanometer scanners offer as vital tools throughout multiple scientific study domains. Their application in biomedical imaging enhances the precision of methods essential for cellular visualization and diagnostics. In material handling, these scanners assist in sophisticated laser cutting and welding procedures, ensuring very little distortion. Furthermore, their duty in environmental surveillance underscores the importance of exact data collection in addressing public health and ecological difficulties. The adaptability and performance of galvanometer scanners continue to drive improvements in these crucial fields.
In laser welding applications, the precision supplied by galvanometer scanners guarantees strong joints with marginal thermal distortion, thereby improving architectural honesty.
In addition, the adaptability of galvanometer scanners to various laser types and wavelengths further broadens their utility in product processing. By achieving high-speed inflection of the laser placement, galvanometer scanners enhance the temporal resolution of these approaches, leading to enhanced imaging and evaluation. The application of galvanometer scanners in laser micromachining enhances the effectiveness and accuracy of this procedure by enabling rapid and accurate light beam positioning.
Galvanometer scanners assist in the dynamic control of laser light beams, making it possible for complex patterns to be etched or cut with high fidelity.
Report this page